food protein induced enterocolitis syndrome treatment
The same is true for the breast-feeding mother if there is a clear connection between breast milk intake and the babys symptoms. Most children outgrow FPIES by age 3 or 4.

Interpretation Of The Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Oral Download Table
Prevention and Management.

. Infants and children appear ill pale and lethargic. If your baby needs formula use hypoallergenic brands that dont have soy or dairy. Steroid treatments may also be used to lessen an immune reaction.
J Allergy Clin Immunol. Usual symptoms include vomiting diarrhoea lethargy and in some cases hypovolemic shock and metabolic acidosis. Treatment for FPIES must be individualized and is often modified as the child grows.
There are no strategies to accelerate development of tolerance in FPIES. Classic symptoms of FPIES include profound vomiting diarrhea and dehydration. This requires careful attention to your childs diet.
Management relies of avoidance of food triggers treatment of accidental exposures and periodic re-evaluations with supervised oral food challenges to monitor for resolution. About Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Written in collaboration by. The FPIES Foundation Board of Directors and Medical Advisory Board Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES is a type of food allergy affecting the gastrointestinal GI tract.
The treatments established were in order of frequency. Usually repetitive up to 1020 times projectile emesis starts within one to three hours after ingestion. Reaction prevention strategies include strict food avoidance until the physician deems a food reintroduction challenge clinically appropriate.
The goal was to examine the demographic characteristics causative foods clinical features treatments and outcomes for children presenting with acute food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome. The recent publication of the First International Consensus Guidelines allowed a positive interaction between different research groups with. Find expert care with an Allergist.
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome can occur in adults. Acute management during reactions includes IV hydration anti-emetics and IV corticosteroids. The primary treatment is strict avoidance of the triggering food.
Oral or intravenous rehydration corticosteroids antihistamines and antiemetics. Unlike most food allergies there is no blood or skin testing available for diagnosis. It was significantly shorter for milk than for solid foods 14 vs.
The only way to prevent a Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES reaction is to strictly avoid the culprit food in the diet. The International FPIES Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Association is a recognized 501c3 nonprofit corporation and organization that provides education support and advocacy for individuals with Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES and. An oral food challenge OFC is sometimes performed to confirm the diagnosis or to determine resolution of the food allergy.
Preparing a letter for potential trips to the ER containing both FPIES information and a list of your childs triggers may be helpful. Also steroids can be used to quell the immune reaction. While the pathophysiology of FPIES is poorly understood the clinical presentation of acute FPEIS reactions has been well characterized.
The preventive diet will only be implemented if at the time of the FPIES. Those treatments will help lessen the FPIES reaction but they wont treat the condition. 1 2 This syndrome is typically characterized by profuse vomiting and lethargy occurring classically 14 hours after ingestion of the offending food.
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is an uncommon and potentially severe non-IgE-mediated food allergy. This was a retrospective study of children with food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome who presented to the Childrens Hospital at Westmead. Although some doctors prescribe epinephrine to stabilize blood pressure before medical treatment the main therapy is to get intravenous fluids.
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a severe presentation of non-IgE-mediated food allergy affecting the gastrointestinal GI tract mainly in infants and young children. 3 Diagnosis of FPIES is difficult. And clinical outcomes are poorly established.
Although CMPA is a common condition encountered in small children chronic forms of FPIES can be difficult to diagnose. The diagnosis of FPIES food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome in the context of cows milk protein allergy CMPA was suspected. Clinical manifestations of food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome.
If a severe reaction does occur treatment includes the administration of intravenous fluids to counteract fluid loss from vomiting and diarrhea. Despite the potential seriousness of reactions awareness of FPIES is low. Symptomatic infants with chronic FPIES improve within 310 days with iv.
Treatment Remove your childs trigger foods from their diet. Dec 24 2021 For a review researchers summarized the most recent research on the nutritional treatment of food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES with an emphasis on the foods implicated and how to avoid them while maintaining a nutritionally sound diet. 12 months P-value002 on average after two episodes.
Steroids may also be given to calm the reaction. Oral food challenges OFCs given at food protein dose. The most common food triggers include soy cows milk and grains.
High-quality studies providing insight into the pathophysiology diagnosis and management are lacking. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non IgE-mediated gastrointestinal food allergy that presents with delayed vomiting after ingestion primarily in infants. Fluids or with hypoallergenic formula18Food reintroduction after a period of avoidance induces acute symptoms.
Oxygen saturation was normal but the laboratory showed important methemoglobinemia. Treatment consists of elimination of the food trigger s from the diet anticipatory guidance regarding complementary feeding periodic reassessments for resolution and managing acute emergencies 6. In the last years the interest of the scientific community toward food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES has grown exponentially.
Mane SK Bahna SL. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. Symptoms may include intractable vomiting diarrhea lethargy pallor abdominal distention hypotension andor shock.
Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES is a non-IgE mediated food allergy most commonly presenting in infants. Food proteininduced enterocolitis FPIES is a non-IgE cell-mediated food allergy that can be severe and lead to shock. In emergency situations the primary treatment for an FPIES episode is intravenous fluids for rehydration.
The best way to manage FPIES is to strictly avoid the food that triggers an allergic reaction. Fernandes BN Boyle RJ Gore C Simpson A Custovic A. Milk soy and grains particularly rice were among the foods linked to FPIES.
Diagnosis time was 76 months on average. We review here the peculiar characteristics of this syndrome.

Managing Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome During The Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology
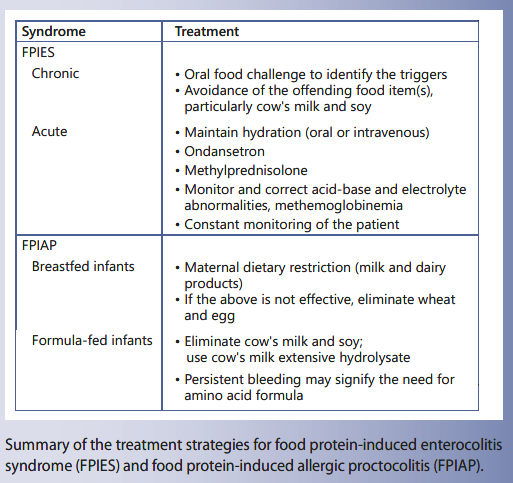
Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome And Proctocolitis

Dietary Management Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome During The Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology

Clinical Types Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Fpies Download Scientific Diagram

Management Of Acute Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Emergencies At Home And In A Medical Facility Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Oral Food Challenge Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Not So Rare After All Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology

Oral Food Challenge In Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Download Table

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology